Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Android - Sending SMS
In Android, you can use SmsManager API or devices Built-in SMS application to send SMS's. In this tutorial, we shows you two basic examples to send SMS message −
SmsManager API
SmsManager smsManager = SmsManager.getDefault();
smsManager.sendTextMessage("phoneNo", null, "sms message", null, null);
Built-in SMS application
Intent sendIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
sendIntent.putExtra("sms_body", "default content");
sendIntent.setType("vnd.android-dir/mms-sms");
startActivity(sendIntent);
Of course, both need SEND_SMS permission.
< uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS" />
Apart from the above method, there are few other important functions available in SmsManager class. These methods are listed below −
| Sr.No. | Method & Description |
| 1 | ArrayList < String > divideMessage(String text) This method divides a message text into several fragments, none bigger than the maximum SMS message size. |
| 2 | static SmsManager getDefault() This method is used to get the default instance of the SmsManager |
| 3 | void sendDataMessage(String destinationAddress, String scAddress, short destinationPort, byte[] data, PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent) This method is used to send a data based SMS to a specific application port. |
| 4 | void sendMultipartTextMessage(String destinationAddress, String scAddress, ArrayList < String > parts, ArrayList < PendingIntent > sentIntents, ArrayList < PendingIntent > deliveryIntents) Send a multi-part text based SMS. |
| 5 | void sendTextMessage(String destinationAddress, String scAddress, String text, PendingIntent sentIntent, PendingIntent deliveryIntent) Send a text based SMS. |
Example
Following example shows you in practical how to use SmsManager object to send an SMS to the given mobile number.
| To experiment with this example, you will need actual Mobile device equipped with latest Android OS, otherwise you will have to struggle with emulator which may not work. |
| Step | Description |
| 1 | You will use Android Studio IDE to create an Android application and name it as tutorialspoint under a package com.example.tutorialspoint. |
| 2 | Modify src/MainActivity.java file and add required code to take care of sending sms. |
| 3 | Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml add any GUI component if required. I'm adding a simple GUI to take mobile number and SMS text to be sent and a simple button to send SMS. |
| 4 | No need to define default string constants at res/values/strings.xml. Android studio takes care of default constants. |
| 5 | Modify AndroidManifest.xml as shown below |
| 6 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
Following is the content of the modified main activity file
src/com.example.tutorialspoint/MainActivity.java
package com.example.tutorialspoint;
import android.Manifest;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v4.app.ActivityCompat;
import android.support.v4.content.ContextCompat;
import android.telephony.SmsManager;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private static final int MY_PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_SEND_SMS =0 ;
Button sendBtn;
EditText txtphoneNo;
EditText txtMessage;
String phoneNo;
String message;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
sendBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSendSMS);
txtphoneNo = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText);
txtMessage = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2);
sendBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
sendSMSMessage();
}
});
}
protected void sendSMSMessage() {
phoneNo = txtphoneNo.getText().toString();
message = txtMessage.getText().toString();
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this,
Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
if (ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(this,
Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS)) {
} else {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this,
new String[]{Manifest.permission.SEND_SMS},
MY_PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_SEND_SMS);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode,String permissions[], int[] grantResults) {
switch (requestCode) {
case MY_PERMISSIONS_REQUEST_SEND_SMS: {
if (grantResults.length > 0
&& grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
SmsManager smsManager = SmsManager.getDefault();
smsManager.sendTextMessage(phoneNo, null, message, null, null);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "SMS sent.",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"SMS faild, please try again.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
}
}
}
}
Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file −
| Here abc indicates about tutorialspoint logo |
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="MainActivity">
< TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Sending SMS Example"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp" />
< TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Mca tutorials "
android:textColor="#ff87ff09"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/imageButton" />
< ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageButton"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
< EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText"
android:hint="Enter Phone Number"
android:phoneNumber="true"
android:textColorHint="@color/abc_primary_text_material_dark"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
< EditText
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/editText"
android:textColorHint="@color/abc_primary_text_material_dark"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/imageButton"
android:hint="Enter SMS" />
< Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Send Sms"
android:id="@+id/btnSendSMS"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="48dp" />
< /RelativeLayout>
Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> < resources> < string name="app_name">tutorialspoint< /string> < /resources>
Following is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml −
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.tutorialspoint" >
< uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS" />
< application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
< activity
android:name="com.example.tutorialspoint.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
< intent-filter>
< action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
< category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
< /intent-filter>
< /activity>
< /application>
< /manifest>
Let's try to run your tutorialspoint application. I assume you have connected your actual Android Mobile device with your computer. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run Eclipse Run  icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Android studio installer will display following window to select an option where you want to run your Android application.
icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Android studio installer will display following window to select an option where you want to run your Android application.

Now you can enter a desired mobile number and a text message to be sent on that number. Finally click on Send SMS button to send your SMS. Make sure your GSM/CDMA connection is working fine to deliver your SMS to its recipient.
You can take a number of SMS separated by comma and then inside your program you will have to parse them into an array string and finally you can use a loop to send message to all the given numbers. That's how you can write your own SMS client. Next section will show you how to use existing SMS client to send SMS.
Using Built-in Intent to send SMS
You can use Android Intent to send SMS by calling built-in SMS functionality of the Android. Following section explains different parts of our Intent object required to send an SMS.
Intent Object - Action to send SMS
You will use ACTION_VIEW action to launch an SMS client installed on your Android device. Following is simple syntax to create an intent with ACTION_VIEW action.
Intent smsIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
Intent Object - Data/Type to send SMS
To send an SMS you need to specify smsto: as URI using setData() method and data type will be to vnd.android-dir/mms-sms using setType() method as follows −
smsIntent.setData(Uri.parse("smsto:"));
smsIntent.setType("vnd.android-dir/mms-sms");
Intent Object - Extra to send SMS
Android has built-in support to add phone number and text message to send an SMS as follows −
smsIntent.putExtra("address" , new String("0123456789;3393993300"));
smsIntent.putExtra("sms_body" , "Test SMS to Angilla");
| Here address and sms_body are case sensitive and should be specified in small characters only. You can specify more than one number in single string but separated by semi-colon (;). |
Example
Following example shows you in practical how to use Intent object to launch SMS client to send an SMS to the given recipients.
| To experiment with this example, you will need actual Mobile device equipped with latest Android OS, otherwise you will have to struggle with emulator which may not work. |
| Step | Description |
| 1 | You will use Android studio IDE to create an Android application and name it as tutorialspoint under a package com.example.tutorialspoint. |
| 2 | Modify src/MainActivity.java file and add required code to take care of sending SMS. |
| 3 | Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml add any GUI component if required. I'm adding a simple button to launch SMS Client. |
| 4 | No need to define default constants.Android studio takes care of default constants. |
| 5 | Modify AndroidManifest.xml as shown below |
| 6 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.tutorialspoint/MainActivity.java.
package com.example.tutorialspoint;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button startBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
startBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
sendSMS();
}
});
}
protected void sendSMS() {
Log.i("Send SMS", "");
Intent smsIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
smsIntent.setData(Uri.parse("smsto:"));
smsIntent.setType("vnd.android-dir/mms-sms");
smsIntent.putExtra("address" , new String ("01234"));
smsIntent.putExtra("sms_body" , "Test ");
try {
startActivity(smsIntent);
finish();
Log.i("Finished sending SMS...", "");
} catch (android.content.ActivityNotFoundException ex) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"SMS faild, please try again later.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file −
| Here abc indicates about tutorialspoint logo |
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
< TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Drag and Drop Example"
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp" />
< TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Mca tutorials "
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:textColor="#ff14be3c" />
< ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_marginTop="48dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
< Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Compose SMS"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_marginTop="54dp"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/imageView" />
< /RelativeLayout>
Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> < resources> < string name="app_name">tutorialspoint< /string> < /resources>
Following is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml −
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.tutorialspoint" >
< application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
< activity
android:name="com.example.tutorialspoint.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
< intent-filter>
< action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
< category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
< /intent-filter>
< /activity>
< /application>
< /manifest>
Let's try to run your tutorialspoint application. I assume you have connected your actual Android Mobile device with your computer. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run Eclipse Run  icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Android studio will display following window to select an option where you want to run your Android application.
icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Android studio will display following window to select an option where you want to run your Android application.
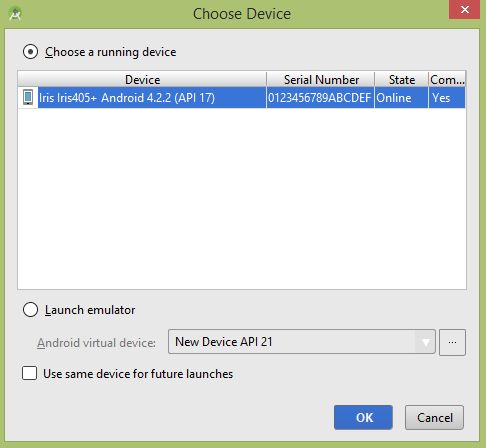
Select your mobile device as an option and then check your mobile device which will display following screen −

Now use Compose SMS button to launch Android built-in SMS clients which is shown below −
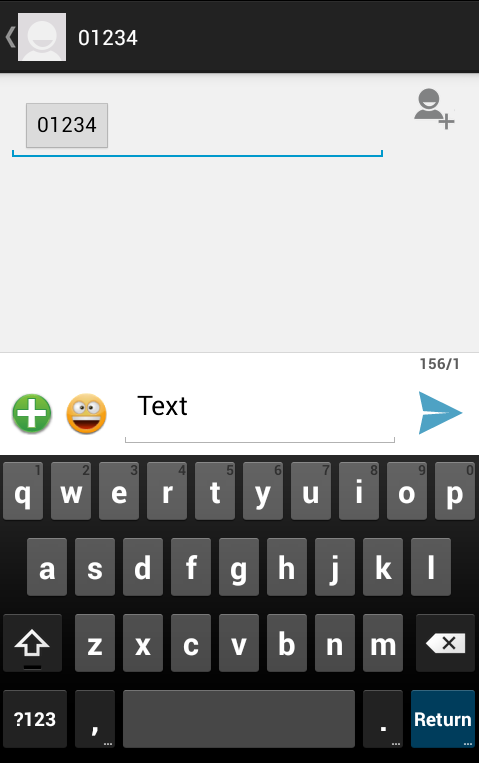
You can modify either of the given default fields and finally use send SMS button to send your SMS to the mentioned recipient.

