Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Sorting a Linked List-1
* r precedes p and s points to the node up to which comparisons are to
be made */
while ( s != start -> link )
{
r = p = start ;
q = p -> link ;
while ( p != s )
{
if ( p -> data > q -> data )
{
if ( p == start )
{
temp = q -> link ;
q -> link = p ;
p -> link = temp ;
start = q ;
r = q ;
}
else
{
temp = q -> link ;
q -> link = p ;
p -> link = temp ;
r -> link = q ;
r = q ;
}
}
else
{
r = p ;
p = p -> link ;
}
q = p -> link ;
if ( q == s )
s = p ;
}
}
}
Let us understand the selection_sort( ) and the bubble_sort( ) functions one by one. In selection_sort( ), pointers p and q point to the nodes being compared and the pointers r and s point to the node prior to p and q respectively. Initially, p and r are set to start, where start is a pointer to the first node in the list. Also, to begin with q and s are set to p -> link. The outer loop is controlled by the condition p -> link != NULL and the inner loop is controlled by the condition q != NULL.
While adjusting the links of the nodes being compared, we would encounter one of the following four cases:
-
Nodes being compared are adjacent to one another and p is pointing to the first node in the list.
-
Nodes being compared are adjacent to one another and p is not pointing to the first node.
-
Nodes being compared are not adjacent to one another and p is pointing to the first node.
-
Nodes being compared are not adjacent to one another and p is not pointing to the first node.
Let us now understand these cases one by one.
Case (a):
When the nodes being compared are adjacent and p is pointing to the first node, the following operations are performed:
p -> link = q -> link ;
q -> link = p ;
temp = p ;
p = q ;
q = temp ;
start = p ;
r = p ;
s = q ;
q = q -> link ;
You can trace these operations with the help of following figure.
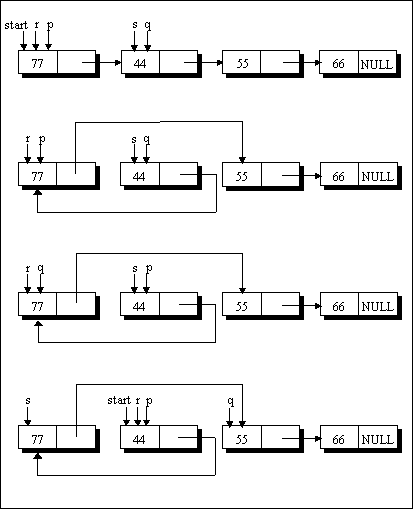
Figure 1
Case (b):
When the nodes being compared are adjacent and p is not pointing to the first node, the following operations are performed:
p -> link = q -> link ;
q -> link = p ;
r -> link = q ;
temp = p ;
p = q ;
q = temp ;
s = q ;
q = q -> link ;
You can trace these operations with the help of Figure 2.
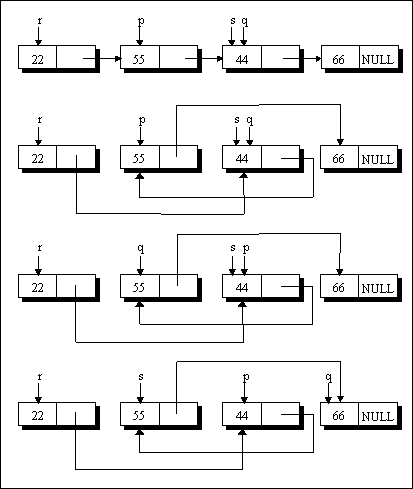
Figure 2
Case (c):
When the nodes being compared are not adjacent and p is pointing to the first node, the following operations are performed:
temp = q -> link ;
q -> link = p -> link ;
p -> link = temp ;
s -> link = p ;
temp = p ;
p = q ;
q = temp ;
s = q ;
q = q -> link ;
start = p ;
You can trace these operations with the help of Figure 3.
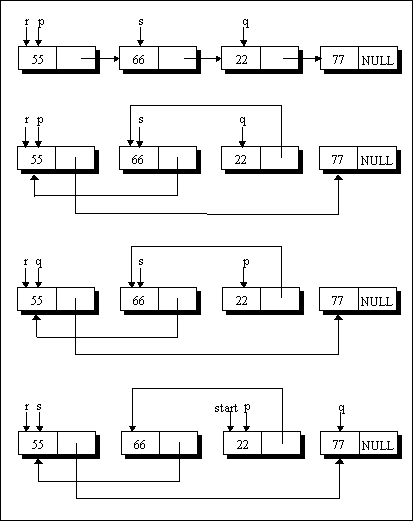
Figure 3

