Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Overview of Database
A Database is a collection of related data organised in a way that data can be easily accessed, managed and updated. Any piece of information can be a data, for example name of your school. Database is actualy a place where related piece of information is stored and various operations can be performed on it.
DBMS
A DBMS is a software that allows creation, definition and manipulation of database. Dbms is actualy a tool used to perform any kind of operation on data in database. Dbms also provides protection and security to database. It maintains data consistency in case of multiple users. Here are some examples of popular dbms, MySql, Oracle, Sybase, Microsoft Access and IBM DB2 etc.
Components of Database System
The database system can be divided into four components.
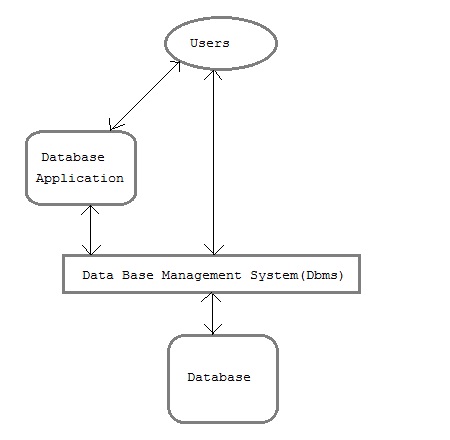
Users : Users may be of various type such as DB administrator, System developer and End users.
Database application : Database application may be Personal, Departmental, Enterprise and Internal
DBMS : Software that allow users to define, create and manages database access, Ex: MySql, Oracle etc.
Database : Collection of logical data.
Functions of DBMS
Provides data Independence
Concurrency Control
Provides Recovery services
Provides Utility services
Provides a clear and logical view of the process that manipulates data.
Advantages of DBMS
Segregation of applicaion program.
Minimal data duplicacy.
Easy retrieval of data.
Reduced development time and maintainance need.
Disadvantages of DBMS
Complexity
Costly
Large in size

