Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Django ModelForm – Create form from Models
Django ModelForm is a class that is used to directly convert a model into a Django form. If you’re building a database-driven app, chances are you’ll have forms that map closely to Django models. For example, a User Registration model and form would have same quality and quantity of model fields and form fields. So instead of creating a redundant code to first create a form and then map it to the model in a view, we can directly use ModelForm. It takes as argument the name of the model and converts it into a Django Form. Not only this, ModelForm offers a lot of methods and features which automate the entire process and help remove code redundancy.
How to convert a model into a Django Form?
To explain the working of the project, we will use project mcatutorials, create a model and map it to Django forms.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
Now when we have our project ready, create a model in mcatutorials/models.py,
# import the standard Django Model
# from built-in library
from django.db import models
# declare a new model with a name "McatutorialsModel"
class McatutorialsModel(models.Model):
# fields of the model
title = models.CharField(max_length = 200)
description = models.TextField()
last_modified = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add = True)
img = models.ImageField(upload_to = "images/")
# renames the instances of the model
# with their title name
def __str__(self):
return self.title
Now, run following commands to create the model,
Python manage.py makemigrations Python manage.py migrate
We can check that model has been successfully created at
http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/mca/mcatutorials/add/,
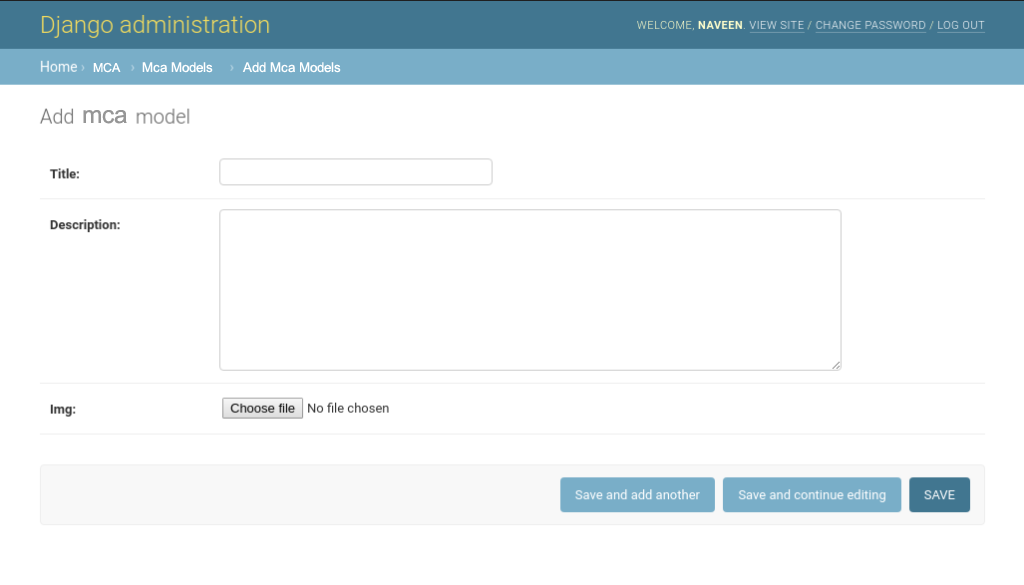
To create a form directly for this model, dive into mcatutorials/forms.py and Enter following code,
# import form class from django
from django import forms
# import McatutorialsModel from models.py
from .models import McaModel
# create a ModelForm
class McaForm(forms.ModelForm):
# specify the name of model to use
class Meta:
model = McaModel
fields = "__all__"
This form takes two arguments fields or exclude>.
- fields – It is strongly recommended that you explicitly set all fields that should be edited in the form using the fields attribute. Failure to do so can easily lead to security problems when a form unexpectedly allows a user to set certain fields, especially when new fields are added to a model. Depending on how the form is rendered, the problem may not even be visible on the web page. Set the fields attribute to the special value ‘__all__’ to indicate that all fields in the model should be used.
- exclude – Set the exclude attribute of the ModelForm’s inner Meta class to a list of fields to be excluded from the form. For example:
class PartialAuthorForm(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Author
exclude = ['title']
Finally, to complete our MVT structure, create a view that would render the form and directly save it to the database. In mca/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render
from .forms import McaForm
def home_view(request):
context ={}
# create object of form
form = McaForm(request.POST or None, request.FILES or None)
# check if form data is valid
if form.is_valid():
# save the form data to model
form.save()
context['form']= form
return render(request, "home.html", context)
Everything set, Now visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/,
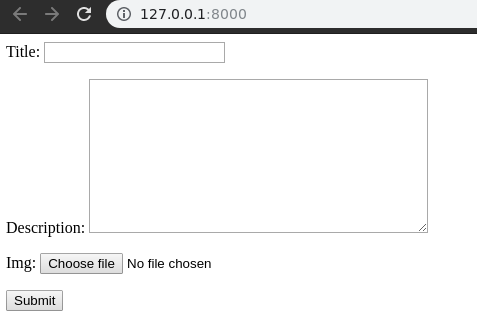
Now you can see that every model field is mapped into a form field and displayed correspondingly. Field mappings are discussed later in this article. So now let’s try entering data into form and check if it gets saved into the database.
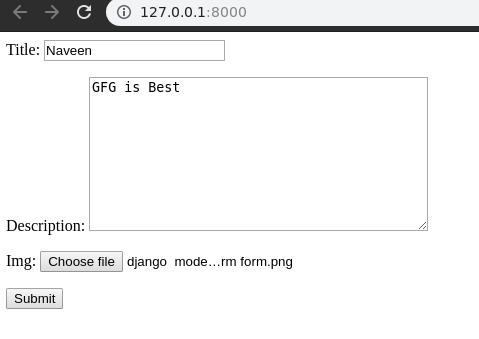
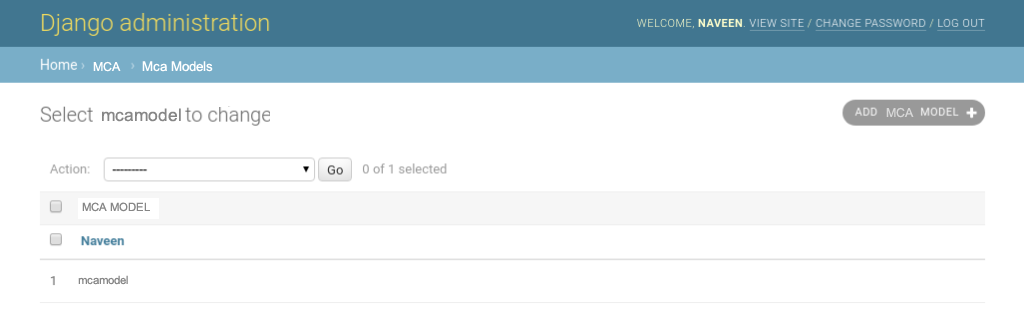
Hit submit and Bingo the form gets saved automatically to database. We can verify it at http://localhost:8000/admin/mca/mcatutorials/.
The generated Form class will have a form field for every model field specified, in the order specified in the fields attribute. Each model field has a corresponding default form field. For example, a CharField on a model is represented as a CharField on a form. A model ManyToManyField is represented as a MultipleChoiceField. Here is the full list of conversions:
| MODEL FIELD | FORM FIELD |
| AutoField | Not represented in the form |
| BigAutoField | Not represented in the form |
| BigIntegerField | IntegerField with min_value set to -9223372036854775808 and max_value set to 9223372036854775807. |
| BinaryField | CharField, if editable is set to True on the model field, otherwise not represented in the form. |
| BooleanField | BooleanField, or NullBooleanField if null=True. |
| CharField | CharField with max_length set to the model field’s max_length and empty_value set to None if null=True. |
| DateField | DateField |
| DateTimeField | DateTimeField |
| DecimalField | DecimalField |
| DurationField | DurationField |
| EmailField | EmailField |
| FileField | FileField |
| FilePathField | FilePathField |
| FloatField | FloatField |
| ForeignKey | ModelChoiceField |
| ImageField | ImageField |
| IntegerField | IntegerField |
| IPAddressField | IPAddressField |
| GenericIPAddressField | GenericIPAddressField |
| ManyToManyField | ModelMultipleChoiceField |
| NullBooleanField | NullBooleanField |
| PositiveIntegerField | IntegerField |
| PositiveSmallIntegerField | IntegerField |
| SlugField | SlugField |
| SmallAutoField | Not represented in the form |
| TextField | CharField with widget=forms.Textarea |
| TimeField | TimeField |
| URLField | URLField |

