Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Django CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) Function Based Views
Django is a Python-based web framework which allows you to quickly create web application without all of the installation or dependency problems that you normally will find with other frameworks. Django is based on MVT (Model View Template) architecture and revolves around CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) operations. CRUD can be best explained as an approach to building a Django web application. In general CRUD means performing Create, Retrieve, Update and Delete operations on a table in a database. Let’s discuss what actually CRUD means,
Create – create or add new entries in a table in the database.
Retrieve – read, retrieve, search, or view existing entries as a list(List View) or retrieve a particular entry in detail (Detail View)
Update – update or edit existing entries in a table in the database
Delete – delete, deactivate, or remove existing entries in a table in the database
Django CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) Function Based ViewsIllustration of How to create and use CRUD view using an Example. Consider a project named mcatutorialshaving an app namedmcatutorials.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
After you have a project and an app, let’s create a model of which we will be creating instances through our view. In mcatutorials/models.py,
# import the standard Django Model
# from built-in library
from django.db import models
# declare a new model with a name "McatutorialsModel"
class McatutorialsModel(models.Model):
# fields of the model
title = models.CharField(max_length = 200)
description = models.TextField()
# renames the instances of the model
# with their title name
def __str__(self):
return self.title
After creating this model, we need to run two commands in order to create Database for the same.
Python manage.py makemigrations Python manage.py migrate
Now we will create a Django ModelForm for this model. Refer this article for more on modelform – Django ModelForm – Create form from Models. create a file forms.py in mcatutorials folder,
from django import forms
from .models import McatutorialsModel
# creating a form
class McatutorialsForm(forms.ModelForm):
# create meta class
class Meta:
# specify model to be used
model = McatutorialsModel
# specify fields to be used
fields = [
"title",
"description",
]
Create View
Create View refers to a view (logic) to create an instance of a table in the database. It is just like taking an input from a user and storing it in a specified table.
In mcatutorials/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render
# relative import of forms
from .models import McatutorialsModel
from .forms import McatutorialsForm
def create_view(request):
# dictionary for initial data with
# field names as keys
context ={}
# add the dictionary during initialization
form = McatutorialsForm(request.POST or None)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
context['form']= form
return render(request, "create_view.html", context)
Create a template in templates/create_view.html,
< form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
< !-- Security token -->
{% csrf_token %}
< !-- Using the formset -->
{{ form.as_p }}
< input type="submit" value="Submit">
< /form>
Now visit http://localhost:8000/
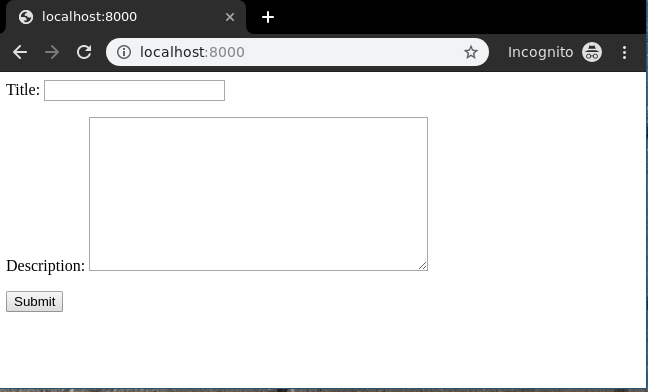
To check complete implementation of Function based Create View, visit Create View – Function based Views Django.
Retrieve ViewRetrieve view is basically divided into two types of views Detail View and List View.
List ViewList View refers to a view (logic) to list all or particular instances of a table from the database in a particular order. It is used to display multiple types of data on a single page or view, for example, products on an eCommerce page. In mcatutorials/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render
# relative import of forms
from .models import McatutorialsModel
def list_view(request):
# dictionary for initial data with
# field names as keys
context ={}
# add the dictionary during initialization
context["dataset"] = McatutorialsModel.objects.all()
return render(request, "list_view.html", context)
Create a template in templates/list_view.html,
< div class="main">
{% for data in dataset %}.
{{ data.title }}< br/>
{{ data.description }}< br/>
< hr/>
{% endfor %}
< /div>
Now visit http://localhost:8000/
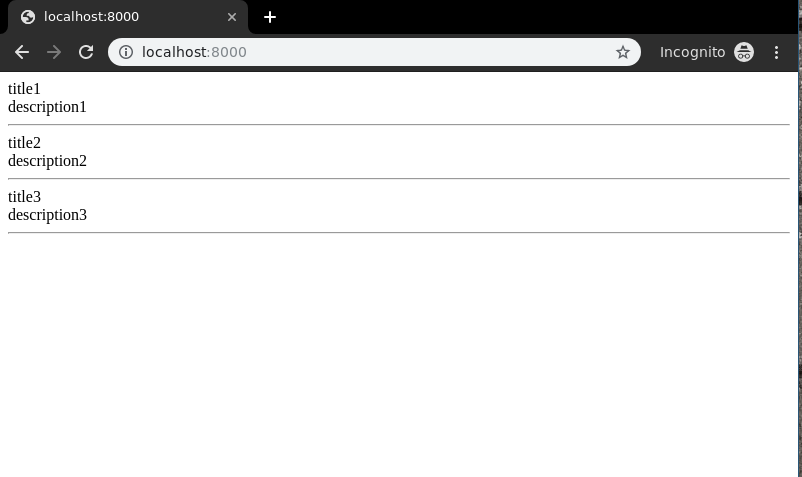
To check complete implementation of Function based List View, visit List View – Function based Views Django
Detail ViewDetail View refers to a view (logic) to display a particular instnace of a table from the database with all the necessary details. It is used to display multiple types of data on a single page or view, for example, profile of a user.
In mcatutorials/views.py,
from django.urls import path
# importing views from views..py
from .views import detail_view
urlpatterns = [
path('< id>', detail_view ),
]
Let’s create a view and template for the same. In mcatutorials/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render
# relative import of forms
from .models import McatutorialsModel
# pass id attribute from urls
def detail_view(request, id):
# dictionary for initial data with
# field names as keys
context ={}
# add the dictionary during initialization
context["data"] = McatutorialsModel.objects.get(id = id)
return render(request, "detail_view.html", context)
Create a template in templates/Detail_view.html,
< div class="main">
< !-- Specify fields to be displayed -->
{{ data.title }}< br/>
{{ data.description }}< br/>
< /div>
Let’s check what is there on http://localhost:8000/1
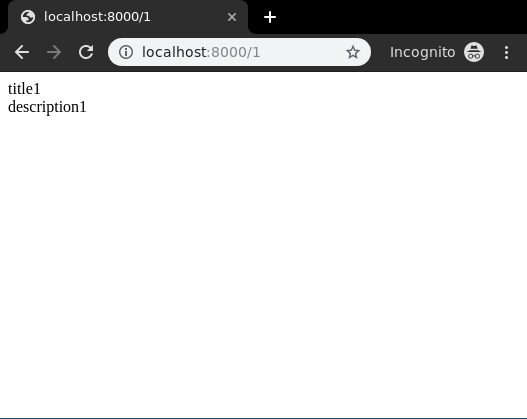
To check complete implementation of Function based Detail View, visit Detail View – Function based Views Django
Update ViewUpdate View refers to a view (logic) to update a particular instance of a table from the database with some extra details. It is used to update enteries in the database for example, updating an article at mcatutorials.
In mcatutorials/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import (get_object_or_404,
render,
HttpResponseRedirect)
# relative import of forms
from .models import McatutorialsModel
from .forms import McatutorialsForm
# after updating it will redirect to detail_View
def detail_view(request, id):
# dictionary for initial data with
# field names as keys
context ={}
# add the dictionary during initialization
context["data"] = McatutorialsModel.objects.get(id = id)
return render(request, "detail_view.html", context)
# update view for details
def update_view(request, id):
# dictionary for initial data with
# field names as keys
context ={}
# fetch the object related to passed id
obj = get_object_or_404(McatutorialsModel, id = id)
# pass the object as instance in form
form = McatutorialsForm(request.POST or None, instance = obj)
# save the data from the form and
# redirect to detail_view
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect("/"+id)
# add form dictionary to context
context["form"] = form
return render(request, "update_view.html", context)
Now create following templates in templates folder, In mcatutorials/templates/update_view.html,
< div class="main">
< !-- Create a Form -->
< form method="POST">
< !-- Security token by Django -->
{% csrf_token %}
< !-- form as paragraph -->
{{ form.as_p }}
< input type="submit" value="Update">
< /form>
< /div>
In mcatutorials/templates/detail_view.html,
< div class="main">
< !-- Display attributes of instance -->
{{ data.title }} < br/>
{{ data.description }}
< /div>
Let’s check if everything is working, visithttp://localhost:8000/1/update.
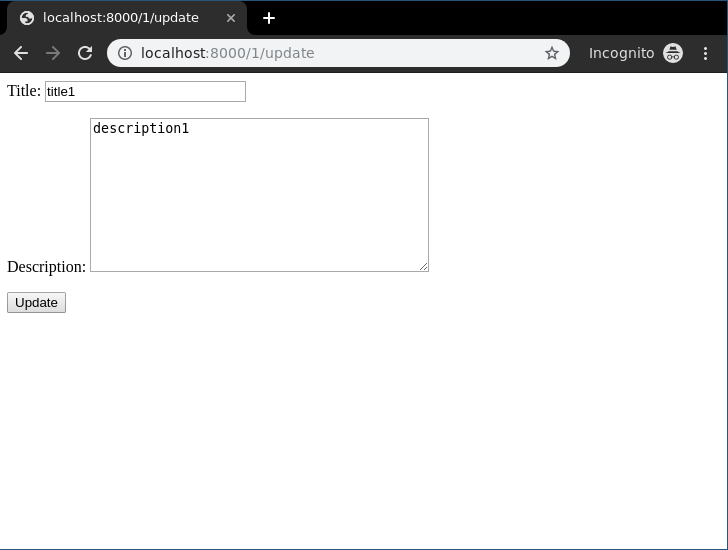
To check complete implementation of Function based update View, visit Update View – Function based Views Django
Delete ViewDelete View refers to a view (logic) to delete a particular instance of a table from the database. It is used to delete entries in the database for example, deleting an article at mcatutorialsformca. In mcatutorials/views.py
from django.shortcuts import (get_object_or_404,
render,
HttpResponseRedirect)
from .models import McatutorialsModel
# delete view for details
def delete_view(request, id):
# dictionary for initial data with
# field names as keys
context ={}
# fetch the object related to passed id
obj = get_object_or_404(McatutorialsModel, id = id)
if request.method =="POST":
# delete object
obj.delete()
# after deleting redirect to
# home page
return HttpResponseRedirect("/")
return render(request, "delete_view.html", context)
Now a url mapping to this view with a regular expression of id, In mcatutorials/urls.py
from django.urls import path
# importing views from views..py
from .views import delete_view
urlpatterns = [
path('< id>/delete', delete_view ),
]
Template for delete view includes a simple form confirming whether user wants to delete the instance or not. In mcatutorials/templates/delete_view.html,
< div class="main">
< !-- Create a Form -->
< form method="POST">
< !-- Security token by Django -->
{% csrf_token %}
Are you want to delete this item ?
< input type="submit" value="Yes" />
< a href="/">Cancel < /a>
< /form>
< /div>
Everything ready, now let’s check if it is working or not, visit http://localhost:8000/2/delete
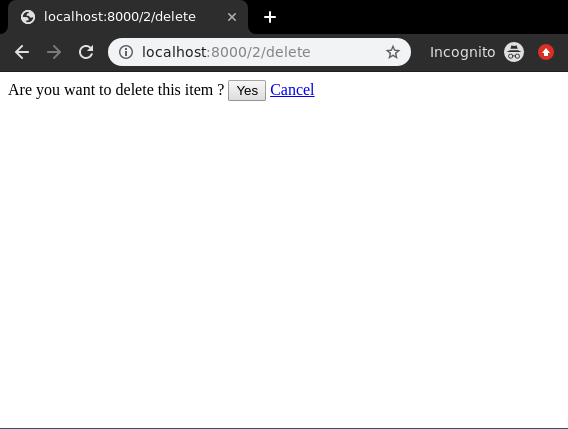
To check complete implementation of Function based Delete View, visit Delete View – Function based Views Django

