Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Django
Django is a Python-based web framework which allows you to quickly create web application without all of the installation or dependency problems that you normally will find with other frameworks.
When you’re building a website, you always need a similar set of components: a way to handle user authentication (signing up, signing in, signing out), a management panel for your website, forms, a way to upload files, etc. Django gives you ready-made components to use.

Why Django?
- Django is a rapid web development framework that can be used to develop fully fleshed web applications in a short period of time.
- It’s very easy to switch database in Django framework.
- It has built-in admin interface which makes easy to work with it.
- Django is fully functional framework that requires nothing else.
- It has thousands of additional packages available.It is very scalable. For more visit When to Use Django? Comparison with other Development Stacks?
Django architecture
Django is based on MVT (Model-View-Template) architecture. MVT is a software design pattern for developing a web application.
MVT Structure has the following three parts –
Model: Model is going to act as the interface of your data. It is responsible for maintaining data. It is the logical data structure behind the entire application and is represented by a database (generally relational databases such as MySql, Postgres).
View: The View is the user interface — what you see in your browser when you render a website. It is represented by HTML/CSS/Javascript and Jinja files.
Template: A template consists of static parts of the desired HTML output as well as some special syntax describing how dynamic content will be inserted.
To check more about Django’s architecture, visit Django Project MVT Structure
Installation of Django
- Install python3 if not installed in your system ( according to configuration of your system and OS) from here . Try to download the latest version of python it’s python3.6.4 this time.
Note-Installation of Django in Linux and Mac is similar, here I am showing it in windows for Linux and mac just open terminal in place of command prompt and go through the following commands.
- Install pip- Open command prompt and enter following command-
python -m pip install -U pip
pip install virtualenv
- Set Virtual environment- Setting up the virtual environment will allow you to edit the dependency which generally your system wouldn’t allow. Follow these steps to set up a virtual environment-
1. Create a virtual environment by giving this command in cmd-
virtualenv env_site
2. Change directory to env_site by this command-
cd env_site
3. Go to Script directory inside env_site and activate virtual environment-
cd Script
activate
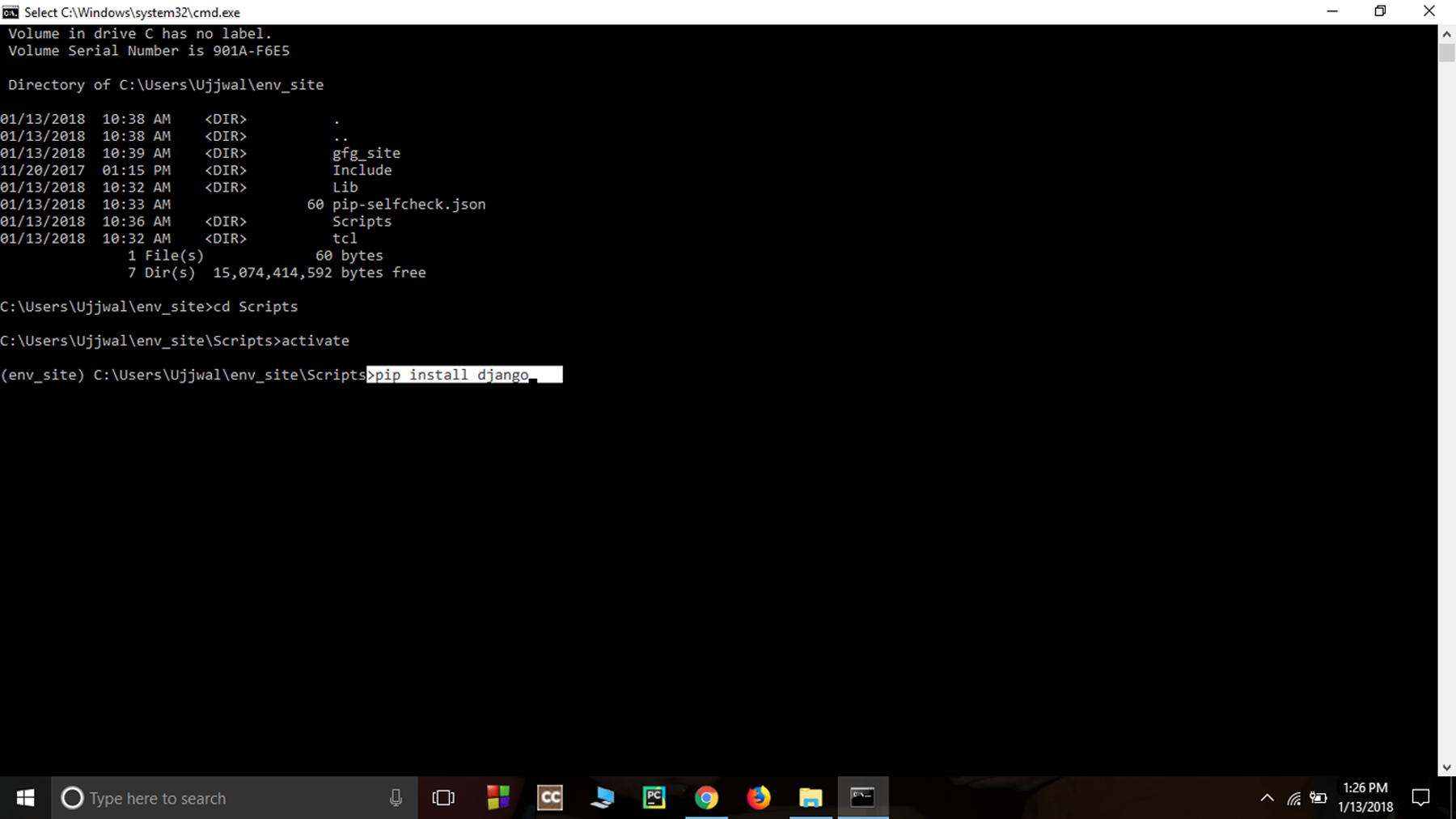
- Install Django- Install django by giving following command-
virtualenv env_site
Creating a Project
Lets’ check how to create a basic project using Django after you have installed it in your pc.
- To initiate a project of Django on Your PC, open Terminal and Enter the following command
django-admin startproject projectName
- A New Folder with name projectName will be created. To enter in the project using terminal enter command
cd projectName
Now run,
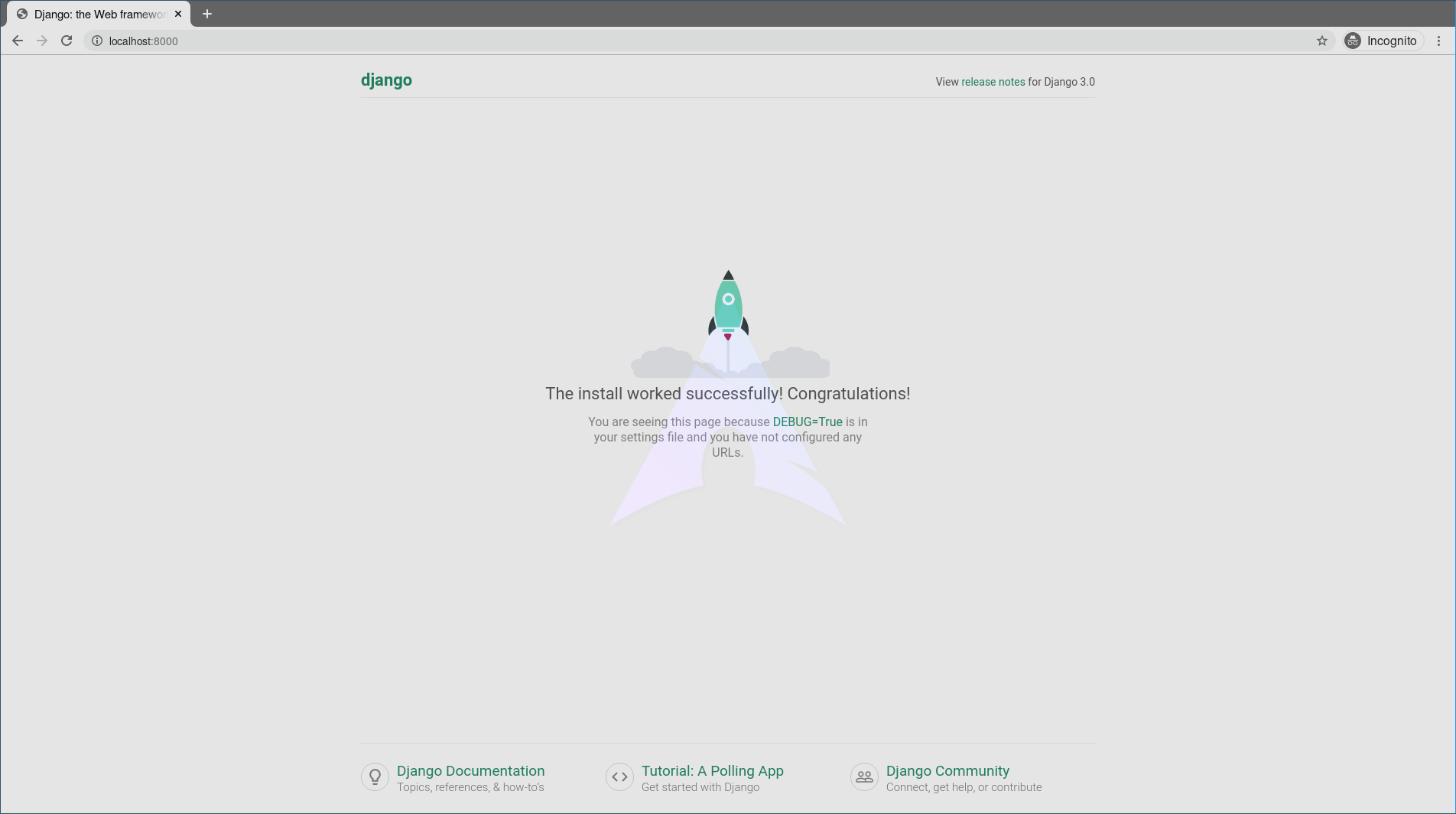
Python manage.py runserver
Now visit http://localhost:8000/,
Creating an App
Django is famous for its unique and fully managed app structure. For every functionality, an app can be created like a completely independent module. This article will take you through how to create a basic app and add functionalities using that app.
- To create a basic app in your Django project you need to go to directory containing manage.py and from there enter the command :
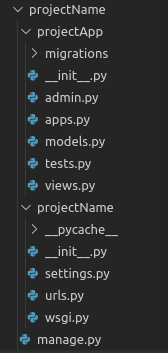
python manage.py startapp projectApp
Now you can see your directory structure as under :
- To consider the app in your project you need to specify your project name in INSTALLED_APPS list as follows in settings.py:
# Application definition
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'projectApp'
]
- So, we have finally created an app but to render the app using urls we need to include the app in our main project so that urls redirected to that app can be rendered. Let us explore it.
Move to projectName-> projectName -> urls.py and add below code in the header
from django.urls import include
Now in the list of URL patterns, you need to specify app name for including your app urls. Here is the code for it –
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
# Enter the app name in following syntax for this to work
path('', include("projectApp.urls")),
]
- Now You can use the default MVT model to create URLs, models, views, etc. in your app and they will be automatically included in your main project.
The main feature of Django Apps is independence, every app functions as an independent unit in supporting the main project. To know more about apps in Django, visit How to Create an App in Django ?

