Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
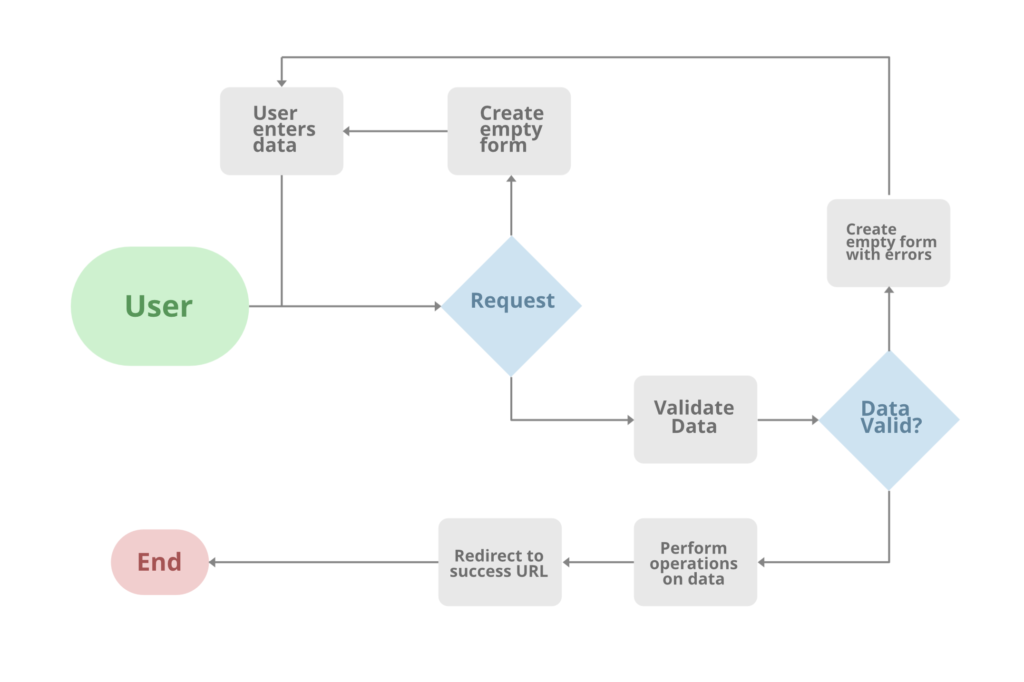
Django Forms
When one creates a Form class, the most important part is defining the fields of the form. Each field has custom validation logic, along with a few other hooks. This article revolves around various fields one can use in a form along with various features and techniques concerned with Django Forms. Forms are basically used for taking input from the user in some manner and using that information for logical operations on databases. For example, Registering a user by taking input as his name, email, password, etc.
Django maps the fields defined in Django forms into HTML input fields. Django handles three distinct parts of the work involved in forms:
- preparing and restructuring data to make it ready for rendering
- creating HTML forms for the data
- receiving and processing submitted forms and data from the client
Note that all types of work done by Django forms can be done with advanced HTML stuff, but Django makes it easier and efficient especially the validation part. Once you get hold of Django forms you will just forget about HTML forms.
Syntax :Django Fields work like Django Model Fields and have the syntax :-
field_name = forms.FieldType(**options)Example –
from django import forms
# creating a form
class McatutorialsForm(forms.Form):
title = forms.CharField()
description = forms.CharField()
Using Django Forms
To use Django Forms, one needs to have a project and an app working in it. After you start an app you can create form in app/forms.py. Before starting to use a form let’s check how to start a project and implement Django Forms.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
Creating a Django Form
Creating a form in Django is completely similar to creating a model, one needs to specify what fields would exist in the form and of what type. For example, to input, a registration form one might need First Name (CharField), Roll Number (IntegerField) and so on.
Syntax
from django import forms
class FormName(models.Model):
# each field would be mapped as an input field in HTML
field_name = models.Field(**options)
To create a form, in mcatutorials/forms.py Enter the code,
# import the standard Django Forms
# from built-in library
from django import forms
# creating a form
class InputForm(forms.Form):
first_name = forms.CharField(max_length = 200)
last_name = forms.CharField(max_length = 200)
roll_number = forms.IntegerField(
help_text = "Enter 6 digit roll number"
)
password = forms.CharField(widget = forms.PasswordInput())
To know more about how to create a Form using Django forms, visit How to create a form using Django Forms ?.
Render Django Forms
Django form fields have several built-in methods to ease the work of the developer but sometimes one needs to implement things manually for customizing User Interface(UI). A form comes with 3 in-built methods that can be used to render Django form fields.
- {{ form.as_table }} will render them as table cells wrapped in < tr> tags
- {{ form.as_p }}will render them wrapped in < p> tags
- {{ form.as_ul }}will render them wrapped in < li> tags
To render this form into a view, move to views.py and create a home_view as below.
from django.shortcuts import render
from .forms import InputForm
# Create your views here.
def home_view(request):
context ={}
context['form']= InputForm()
return render(request, "home.html", context)
In view one needs to just create an instance of the form class created above in forms.py.
Now let’s edit templates > home.html
< form action = "" method = "post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{form }}
< input type="submit" value=Submit">
< /form>
Now, visit http://localhost:8000/
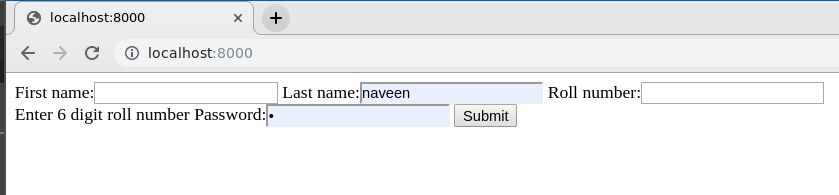
To check how to use the data rendered by Django Forms visit Render Django Form Fields
Create Django Form from ModelsDjango ModelForm is a class that is used to directly convert a model into a Django form. If you’re building a database-driven app, chances are you’ll have forms that map closely to Django models. Now when we have our project ready, create a model in mcatutorials/models.py,
# import the standard Django Model
# from built-in library
from django.db import models
# declare a new model with a name "McaModel"
class McaModel(models.Model):
# fields of the model
title = models.CharField(max_length = 200)
description = models.TextField()
last_modified = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add = True)
img = models.ImageField(upload_to = "images/")
# renames the instances of the model
# with their title name
def __str__(self):
return self.title
To create a form directly for this model, dive into mcatutorials/forms.py and Enter following code,
# import form class from django
from django import forms
# import McaModel from models.py
from .models import McatutorialsModel
# create a ModelForm
class McaForm(forms.ModelForm):
# specify the name of model to use
class Meta:
model = McaModel
fields = "__all__"
Now visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/,
More on Django Forms- Render HTML Forms (GET & POST) in Django
- {{ form.as_p }} – Render Django Forms as paragraph
- {{ form.as_table }} – Render Django Forms as table
- {{ form.as_ul }} – Render Django Forms as list
- Django form field custom widgets
- Python | Form validation using django
- Django ModelForm – Create form from Models
- Render Django Form Fields Manually
- Django Formsets
- Django ModelFormSets
Basic form data types and fields list
The most important part of a form and the only required part is the list of fields it defines. Fields are specified by class attributes. Here is a list of all Form Field types used in Django.
| NAME | CLASS | HTML INPUT |
| BooleanField | class BooleanField(**kwargs) | CheckboxInput |
| CharField | class CharField(**kwargs) | TextInput |
| ChoiceField | class ChoiceField(**kwargs) | Select |
| TypedChoiceField | class TypedChoiceField(**kwargs) | Select |
| DateField | class DateField(**kwargs) | DateInput |
| DateTimeField | class DateTimeField(**kwargs) | DateTimeInput |
| DecimalField | class DecimalField(**kwargs) | NumberInput when Field.localize is False, else TextInput |
| DurationField | class DurationField(**kwargs) | TextInput |
| EmailField | class EmailField(**kwargs | EmailInput |
| FileField | class FileField(**kwargs) | ClearableFileInput |
| FilePathField | class FilePathField(**kwargs) | Select |
| FloatField | class FloatField(**kwargs) | NumberInput when Field.localize is False, else TextInput |
| ImageField | class ImageField(**kwargs) | ClearableFileInput |
| IntegerField | class IntegerField(**kwargs) | NumberInput when Field.localize is False, else TextInput |
| GenericIPAddressField | class GenericIPAddressField(**kwargs) | TextInput |
| MultipleChoiceField | class MultipleChoiceField(**kwargs) | SelectMultiple |
| TypedMultipleChoiceField | class TypedMultipleChoiceField(**kwargs) | SelectMultiple |
| NullBooleanField | class NullBooleanField(**kwargs) | NullBooleanSelect |
| RegexField | class RegexField(**kwargs) | TextInput |
| SlugField | class SlugField(**kwargs) | TextInput |
| TimeField | class TimeField(**kwargs) | TimeInput |
| URLField | class URLField(**kwargs) | URLInput |
| UUIDField | class UUIDField(**kwargs) | TextInput |
Core Field Arguments
Core Field arguments are the arguments given to each field for applying some constraint or imparting a particular characteristic to a particular Field. For example, adding an argument required = False to CharField will enable it to be left blank by the user. Each Field class constructor takes at least these arguments. Some Field classes take additional, field-specific arguments, but the following should always be accepted:
| FIELD OPTIONS | DESCRIPTION |
| required | By default, each Field class assumes the value is required, so to make it not required you need to set required=False |
| label | The label argument lets you specify the “human-friendly” label for this field. This is used when the Field is displayed in a Form. |
| label_suffix | The label_suffix argument lets you override the form’s label_suffix on a per-field basis. |
| widget | The widget argument lets you specify a Widget class to use when rendering this Field. See Widgets for more information. |
| help_text | The help_text argument lets you specify descriptive text for this Field. If you provide help_text, it will be displayed next to the Field when the Field is rendered by one of the convenience Form methods. |
| error_messages | The error_messages argument lets you override the default messages that the field will raise. Pass in a dictionary with keys matching the error messages you want to override. |
| validators | The validators argument lets you provide a list of validation functions for this field. |
| localize | The localize argument enables the localization of form data input, as well as the rendered output. |
| disabled. | The disabled boolean argument, when set to True, disables a form field using the disabled HTML attribute so that it won’t be editable by users. |

