Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
System Bus in Computers
A computer bus transfers data between components of a computer system. A system bus is a single computer bus for the data transfer between the central processing unit and the memory. The transfer speed of the system bus is a critical element of the overall performance of a computer.
We also recommend watching How Star, Bus, Ring & Mesh Topology Connect Computer Networks in Organizations and Computer System Components: Computer Parts & Functions
Definitions
A computer system consists of a central processing unit (CPU) for processing data, main memory to store the data being processed and multiple input and output devices. There various components have to be connected to each other for the transfer of data. A computer bus is a subsystem of the computer that makes these transfers happen. In early computer systems all transfers used actual cables. Large bundles of wires were organized using 'bus bars,' which is where the term bus comes from.
Cables are still used in present-day computer systems, in particular to connect external devices. The most common type of connection is a Universal Serial Bus (USB). Many peripheral devices, such as printers and scanners, use a USB connection. Transfers between internal components of a computer can also use cables, but some types have been replaced by integrated electronic circuitry, such as those found on a motherboard.
The most critical connection of any computer system is the system bus. This is a single computer bus that controls the transfers between the CPU, the main memory, and the input/output devices.
How The System Bus Works
The system bus carries three types of information: address, data, and control. The address information describes where data is located and where it needs to go during a particular operation. The data are the actual digital pieces of information that need to be transferred. The control information manages the flow of the address and data information, including the direction of the transfer and exactly how data needs to be routed through the computer system. Because of these three different types of information, the system bus actually consists of three buses, as illustrated in the figure below.
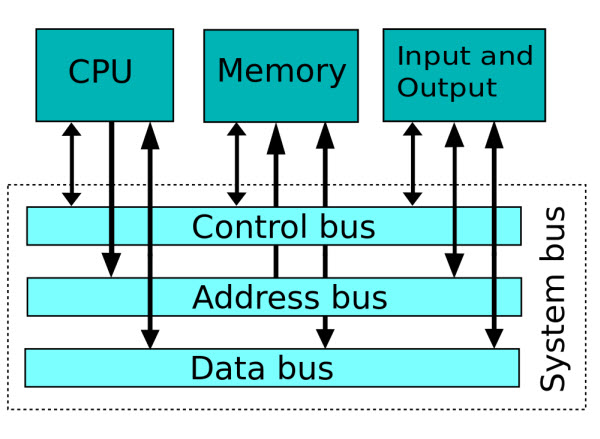
The general design of a single system bus
The system bus is like the internal transportation system of your computer. Consider the following example. You want to listen to some music that is residing on your hard disk drive as an MP3 file. So the MP3 file is the data. These data have to be transferred to the sound card and converted to an analog signal so you can listen to it on your speakers. So the address information is the location of the MP3 file on your hard disk and the location of your sound card. The control information manages how this transfer is going to take place - which direction and through which components. All of this is managed by the brains of your computer (the CPU), but the system bus makes the actual transfers happen.

