Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
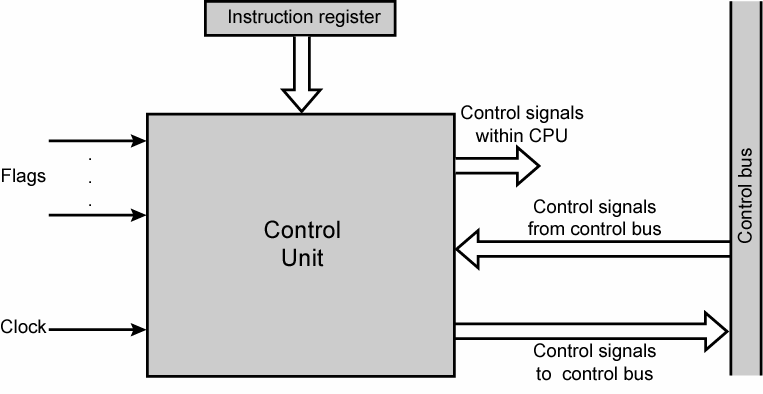
Control Unit
A CU takes its input from the instruction and status registers. Its rules of operation, or microprogram, are encoded in a programmable logic array (PLA), random logic or read-only memory (ROM).
CU functions are as follows:
- Controls sequential instruction execution
- Interprets instructions
- Guides data flow through different computer areas
- Regulates and controls processor timing
- Sends and receives control signals from other computer devices
- Handles multiple tasks, such as fetching, decoding, execution handling and storing results
CUs are designed in two ways:
- Hardwired control: Design is based on a fixed architecture. The CU is made up of flip-flops, logic gates, digital circuits and encoder and decoder circuits that are wired in a specific and fixed way. When instruction set changes are required, wiring and circuit changes must be made. This is preferred in a reduced instruction set computing (RISC) architecture, which only has a small number of instructions.
- Microprogram control: Microprograms are stored in a special control memory and are based on flowcharts. They are replaceable and ideal because of their simplicity