Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Arduino - Due & Zero
The Arduino Due is a microcontroller board based on the Atmel SAM3X8E ARM Cortex-M3 CPU. It is the first Arduino board based on a 32-bit ARM core microcontroller. Important features −
-
It has 54 digital input/output pins (of which 12 can be used as PWM outputs)
12 analog inputs
4 UARTs (hardware serial ports)
84 MHz clock, an USB OTG capable connection
2 DAC (digital to analog), 2 TWI, a power jack, an SPI header, a JTAG header
Reset button and an erase button
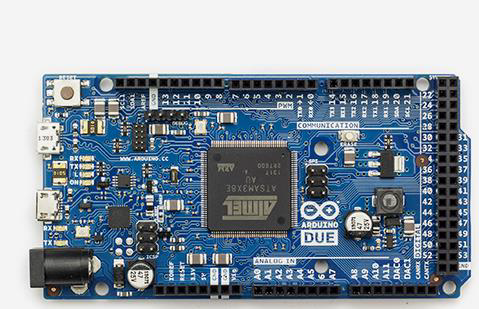
Characteristics of the Arduino Due Board
| Operating volt | CPU speed | Analog in/out | Digital IO/ PWM | EEPROM [KB] | SRAM [KB] | Flash [KB] | USB | UART |
| 3.3 Volt | 84 Mhz | 12/2 | 54/12 | - | 96 | 512 | 2 micro | 4 |
Communication
-
4 Hardware UARTs
2 I2C
1 CAN Interface (Automotive communication protocol)
1 SPI
1 Interface JTAG (10 pin)
1 USB Host (like as Leonardo)
1 Programming Port
Unlike most Arduino boards, the Arduino Due board runs at 3.3V. The maximum voltage that the I/O pins can tolerate is 3.3V. Applying voltages higher than 3.3V to any I/O pin could damage the board.
The board contains everything needed to support the microcontroller. You can simply connect it to a computer with a micro-USB cable or power it with an AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started. The Due is compatible with all Arduino shields that work at 3.3V.
Arduino Zero
The Zero is a simple and powerful 32-bit extension of the platform established by the UNO. The Zero board expands the family by providing increased performance, enabling a variety of project opportunities for devices, and acts as a great educational tool for learning about 32-bit application development.
Important features are −
-
The Zero applications span from smart IoT devices, wearable technology, high-tech automation, to crazy robotics.
The board is powered by Atmel’s SAMD21 MCU, which features a 32-bit ARM Cortex® M0+ core.
One of its most important features is Atmel’s Embedded Debugger (EDBG), which provides a full debug interface without the need for additional hardware, significantly increasing the ease-of-use for software debugging.
EDBG also supports a virtual COM port that can be used for device and bootloader programming.
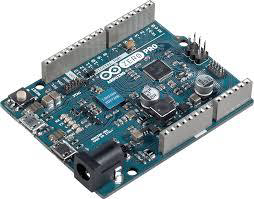
Characteristics of the Arduino Zero board
| Operating volt | CPU speed | Analog in/out | Digital IO/ PWM | EEPROM [KB] | SRAM [KB] | Flash [KB] | USB | UART |
| 3.3 Volt | 48 Mhz | 6/1 | 14/10 | - | 32 | 256 | 2 micro | 2 |
Unlike most Arduino and Genuino boards, the Zero runs at 3.3V. The maximum voltage that the I/O pins can tolerate is 3.3V. Applying voltages higher than 3.3V to any I/O pin could damage the board.
The board contains everything needed to support the microcontroller. You can simply connect it to a computer with a micro-USB cable or power it with an AC-to-DC adapter or a battery to get started. The Zero is compatible with all the shields that work at 3.3V.

