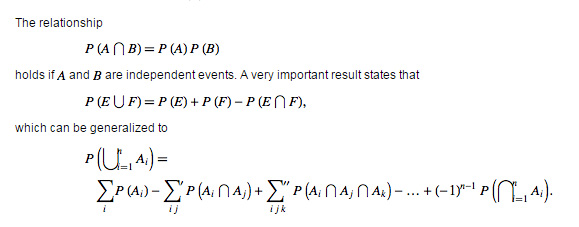Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics that studies the possible outcomes of given events together with the outcomes' relative likelihoods and distributions. In common usage, the word "probability" is used to mean the chance that a particular event (or set of events) will occur expressed on a linear scale from 0 (impossibility) to 1 (certainty), also expressed as a percentage between 0 and 100%. The analysis of events governed by probability is called statistics.
There are several competing interpretations of the actual "meaning" of probabilities. Frequentists view probability simply as a measure of the frequency of outcomes (the more conventional interpretation), while Bayesians treat probability more subjectively as a statistical procedure that endeavors to estimate parameters of an underlying distribution based on the observed distribution.
A properly normalized function that assigns a probability "density" to each possible outcome within some interval is called a probability density function (or probability distribution function), and its cumulative value (integral for a continuous distribution or sum for a discrete distribution) is called a distribution function (or cumulative distribution function).
A variate is defined as the set of all random variables that obey a given probabilistic law. It is common practice to denote a variate with a capital letter (most commonly X). The set of all values that X can take is then called the range, denoted R_X (Evans et al. 2000, p. 5). Specific elements in the range of X are called quantiles and denoted x, and the probability that a variate X assumes the element x is denoted P(X=x).
Probabilities are defined to obey certain assumptions, called the probability axioms. Let a sample space contain the union ( union ) of all possible events E_i, so