Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
- Dart Programming
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Dart Programming - Environment
This chapter discusses setting up the execution environment for Dart on the Windows platform.
Executing Script Online with DartPad
You may test your scripts online by using the online editor at https://dartpad.dartlang.org/. The Dart Editor executes the script and displays both HTML as well as console output. The online editor is shipped with a set of preset code samples.
A screenshot of the Dartpad editor is given below −
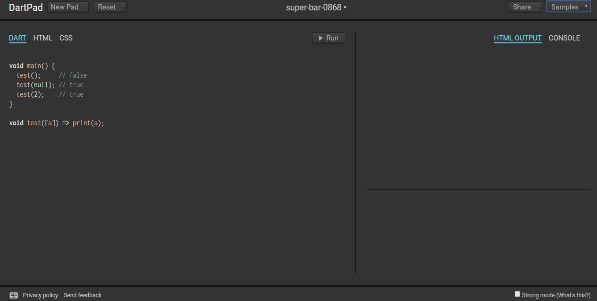
Dartpad also enables to code in a more restrictive fashion. This can be achieved by checking the Strong mode option on the bottom right of the editor. Strong mode helps with −
Stronger static and dynamic checking
Idiomatic JavaScript code generation for better interoperability.
You may try the following example using Dartpad
void main() {
print('hello world');
}
The code will display the following output
hello world
Setting Up the Local Environment
In this section, let us see how to set up the local environment.
Using the Text Editor
Examples of a few editors include Windows Notepad, Notepad++, Emacs, vim or vi, etc. Editors may vary from one Operating System to another. The source files are typically named with the extension ".dart".
Installing the Dart SDK
The current stable version of Dart is 1.21.0. The dart sdk can be downloaded from −
https://www.dartlang.org/install/archive
http://www.gekorm.com/dart-windows/
A screenshot of the Dart SDK installation is given below −
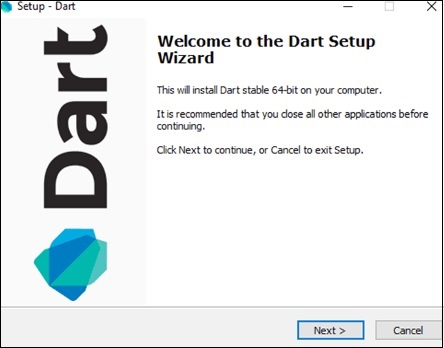
On completion of the SDK installation, set the PATH environment variable to −
< dart-sdk-path>\bin
Verifying the Installation
To verify if Dart has been successfully installed, open the command prompt and enter the following command −
Dart
If installation is successful, it will show the dart runtime.
IDE Support
A plethora of IDEs support scripting in Dart. Examples include Eclipse, IntelliJ, and WebStorm from Jet brains.
Given below are the steps for configuring the Dart environment using WebStrom IDE.
Installing WebStorm
The installation file for WebStorm can be downloaded from https://www.jetbrains.com/webstorm/download/#section=windows-version.
The WebStorm installation file is available for Mac OS, Windows and Linux.
After downloading the installation files, follow the steps given below −
Install the Dart SDK: Refer to the steps listed above
Create a new Dart project and configure Dart support
To create a new Dart project,
Click Create New Project from the Welcome Screen
In the next dialog box, click Dart
If there is no value specified for the Dart SDK path, then provide the SDK path. For example, the SDK path may be < dart installation directory>/dart/dartsdk.
Add a Dart File to the Project
To add a Dart file to the Project −
Right-click on the Project
New → Dart File
Enter the name of the Dart Script
A screenshot of the WebStorm Editor is given below −
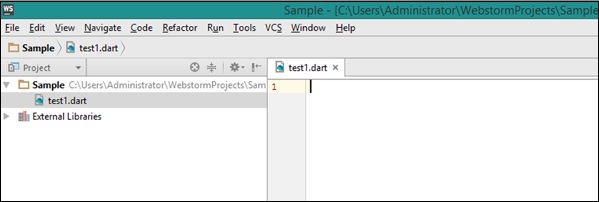
The dart2js Tool
The dart2js tool compiles Dart code to JavaScript. Compiling Dart code to JS enables running the Dart script on browsers that do not support the Dart VM.
The dart2js tool is shipped as a part of the Dart SDK and can be found in the /dartsdk/bin folder.
To compile Dart to JavaScript, type the following command in the terminal
dart2js - - out = < output_file>.js < dart_script>.dart
This command produces a file that contains the JavaScript equivalent of your Dart code. A complete tutorial on using this utility can be found on the official Dart website.

