Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Protocol and standards-2
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is simplest Transport Layer communication protocol available of the TCP/IP protocol suite. It involves minimum amount of communication mechanism. UDP is said to be an unreliable transport protocol but it uses IP services which provides best effort delivery mechanism.
In UDP, the receiver does not generate an acknowledgement of packet received and in turn, the sender does not wait for any acknowledgement of packet sent. This shortcoming makes this protocol unreliable as well as easier on processing.
Requirement of UDP
A question may arise, why do we need an unreliable protocol to transport the data? We deploy UDP where the acknowledgement packets share significant amount of bandwidth along with the actual data. For example, in case of video streaming, thousands of packets are forwarded towards its users. Acknowledging all the packets is troublesome and may contain huge amount of bandwidth wastage. The best delivery mechanism of underlying IP protocol ensures best efforts to deliver its packets, but even if some packets in video streaming get lost, the impact is not calamitous and can be ignored easily. Loss of few packets in video and voice traffic sometimes goes unnoticed.
Features
UDP is used when acknowledgement of data does not hold any significance.
UDP is good protocol for data flowing in one direction.
UDP is simple and suitable for query based communications.
UDP is not connection oriented.
UDP does not provide congestion control mechanism.
UDP does not guarantee ordered delivery of data.
UDP is stateless.
UDP is suitable protocol for streaming applications such as VoIP, multimedia streaming.
UDP Header
UDP header is as simple as its function.
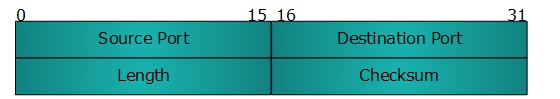
UDP header contains four main parameters:
Source Port - This 16 bits information is used to identify the source port of the packet.
Destination Port - This 16 bits information, is used identify application level service on destination machine.
Length - Length field specifies the entire length of UDP packet (including header). It is 16-bits field and minimum value is 8-byte, i.e. the size of UDP header itself.
Checksum - This field stores the checksum value generated by the sender before sending. IPv4 has this field as optional so when checksum field does not contain any value it is made 0 and all its bits are set to zero.
UDP application
Here are few applications where UDP is used to transmit data:
Domain Name Services
Simple Network Management Protocol
Trivial File Transfer Protocol
Routing Information Protocol
Kerberos
There are several protocols which work for users in Application Layer. Application layer protocols can be broadly divided into two categories:
Protocols which are used by users.For email for example, eMail.
Protocols which help and support protocols used by users.For example DNS.
Few of Application layer protocols are described below:
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) works on Client Server model. It uses UDP protocol for transport layer communication. DNS uses hierarchical domain based naming scheme. The DNS server is configured with Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) and email addresses mapped with their respective Internet Protocol addresses.
A DNS server is requested with FQDN and it responds back with the IP address mapped with it. DNS uses UDP port 53.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is used to transfer electronic mail from one user to another. This task is done by means of email client software (User Agents) the user is using. User Agents help the user to type and format the email and store it until internet is available. When an email is submitted to send, the sending process is handled by Message Transfer Agent which is normally comes inbuilt in email client software.
Message Transfer Agent uses SMTP to forward the email to another Message Transfer Agent (Server side). While SMTP is used by end user to only send the emails, the Servers normally use SMTP to send as well as receive emails. SMTP uses TCP port number 25 and 587.
Client software uses Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) or POP protocols to receive emails.
File Transfer Protocol
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is the most widely used protocol for file transfer over the network. FTP uses TCP/IP for communication and it works on TCP port 21. FTP works on Client/Server Model where a client requests file from Server and server sends requested resource back to the client.
FTP uses out-of-band controlling i.e. FTP uses TCP port 20 for exchanging controlling information and the actual data is sent over TCP port 21.
The client requests the server for a file. When the server receives a request for a file, it opens a TCP connection for the client and transfers the file. After the transfer is complete, the server closes the connection. For a second file, client requests again and the server reopens a new TCP connection.
Post Office Protocol (POP)
The Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP 3) is a simple mail retrieval protocol used by User Agents (client email software) to retrieve mails from mail server.
When a client needs to retrieve mails from server, it opens a connection with the server on TCP port 110. User can then access his mails and download them to the local computer. POP3 works in two modes. The most common mode the delete mode, is to delete the emails from remote server after they are downloaded to local machines. The second mode, the keep mode, does not delete the email from mail server and gives the user an option to access mails later on mail server.
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
The Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the foundation of World Wide Web. Hypertext is well organized documentation system which uses hyperlinks to link the pages in the text documents. HTTP works on client server model. When a user wants to access any HTTP page on the internet, the client machine at user end initiates a TCP connection to server on port 80. When the server accepts the client request, the client is authorized to access web pages.
To access the web pages, a client normally uses web browsers, who are responsible for initiating, maintaining, and closing TCP connections. HTTP is a stateless protocol, which means the Server maintains no information about earlier requests by clients.
HTTP versions
HTTP 1.0 uses non persistent HTTP. At most one object can be sent over a single TCP connection.
HTTP 1.1 uses persistent HTTP. In this version, multiple objects can be sent over a single TCP connection.

