Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
IOT - Working
1. Objective
In the last IoT tutorial, we introduced hardware and software used in IoT. Today, we will study how IoT works or How the Internet of Things works. Moreover, we will the IoT components. In addition, we will see some real-time example of how IoT works.
So, let’s begin with how IoT works.
2. How IoT Works?
Just like Internet has changed the way we work & communicate with each other, by connecting us through the World Wide Web (internet), IoT also aims to take this connectivity to another level by connecting multiple devices at a time to the internet thereby facilitating man to machine and machine to machine interactions.
People who came up with this idea, have also realized that this IoT ecosystem is not limited to a particular field but has business applications in areas of home automation, vehicle automation, factory line automation, medical, retail, healthcare and more.

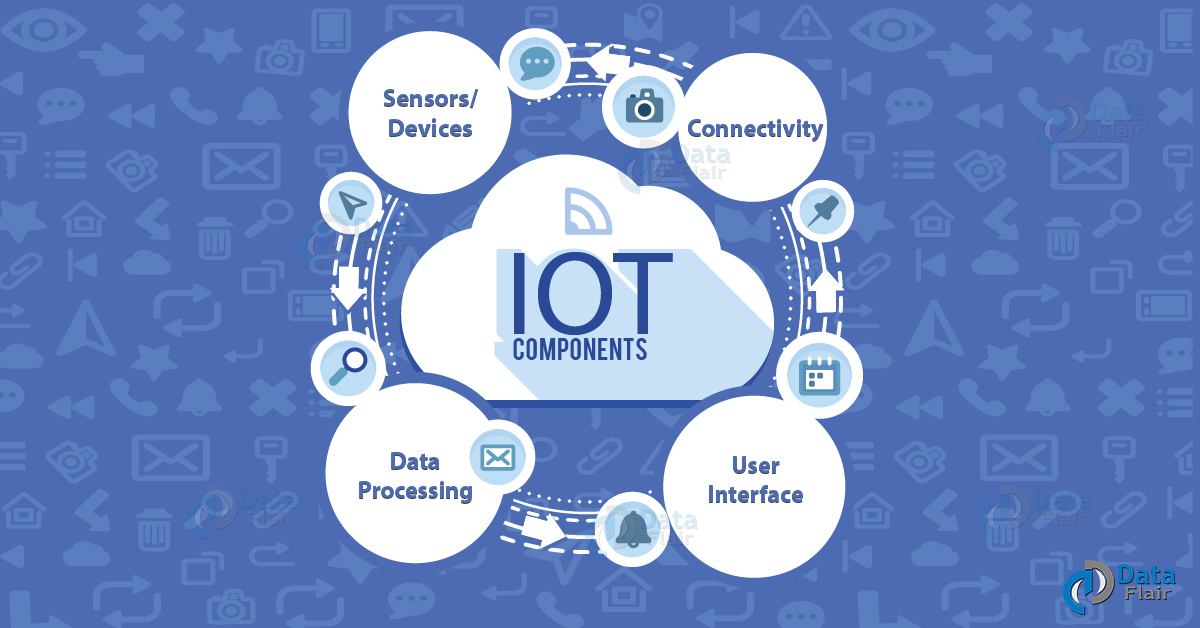
a. IoT Components
Here, 4 fundamental components of IoT system, which tells us how IoT works.
i. Sensors/Devices
First, sensors or devices help in collecting very minute data from the surrounding environment. All of this collected data can have various degrees of complexities ranging from a simple temperature monitoring sensor or a complex full video feed.
A device can have multiple sensors that can bundle together to do more than just sense things. For example, our phone is a device that has multiple sensors such as GPS, accelerometer, camera but our phone does not simply sense things.
The most rudimentary step will always remain to pick and collect data from the surrounding environment be it a standalone sensor or multiple devices.
ii. Connectivity
Next, that collected data is sent to a cloud infrastructure but it needs a medium for transport.
The sensors can be connected to the cloud through various mediums of communication and transports such as cellular networks, satellite networks, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, wide-area networks (WAN), low power wide area network and many more.
Every option we choose has some specifications and trade-offs between power consumption, range, and bandwidth. So, choosing the best connectivity option in the IOT system is important.

iii. Data Processing
Once the data is collected and it gets to the cloud, the software performs processing on the acquired data.
This can range from something very simple, such as checking that the temperature reading on devices such as AC or heaters is within an acceptable range. It can sometimes also be very complex, such as identifying objects (such as intruders in your house) using computer vision on video. But there might be a situation when a user interaction is required, example- what if when the temperature is too high or if there is an intruder in your house? That’s where the user comes into the picture.
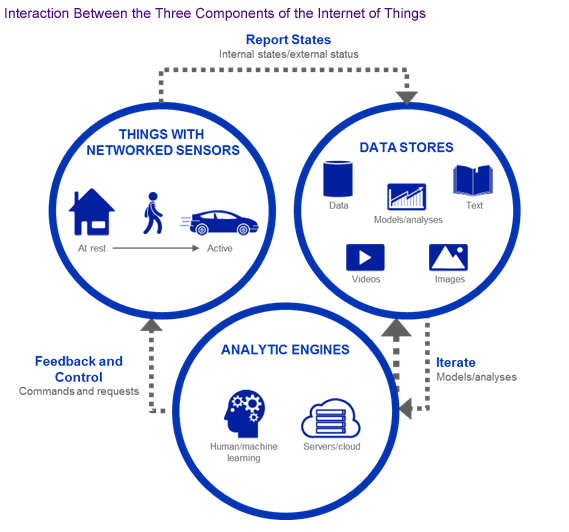
iv. User Interface
Next, the information made available to the end-user in some way. This can achieve by triggering alarms on their phones or notifying through texts or emails.
Also, a user sometimes might also have an interface through which they can actively check in on their IOT system. For example, a user has a camera installed in his house, he might want to check the video recordings and all the feeds through a web server.
However, it’s not always this easy and a one-way street. Depending on the IoT application and complexity of the system, the user may also be able to perform an action that may backfire and affect the system. For example, if a user detects some changes in the refrigerator, the user can remotely adjust the temperature via their phone.
There are also cases where some actions perform automatically. By establishing and implementing some predefined rules, the entire IOT system can adjust the settings automatically and no human has to be physically present. Also in case if any intruders are sensed, the system can generate an alert not only to the owner of the house but to the concerned authorities.
3. Real Life Example Depicting Working of IoT
Here, we will discuss some examples, which states how IoT works in real-life:
i. Say, we have an AC in our room, now the temperature sensor installed in it in the room will be integrated with a gateway. A gateway’s purpose is to help connect the temperature sensor (inside the AC) to the Internet by making use of a cloud infrastructure.
ii. A Cloud/server infrastructure has detailed records about each and every device connected to it such as device id, a status of the device, what time was the device last accessed, number of times the device has been accessed and much more.
iii. A connection with the cloud then implement by making use of web services such as RESTful.
iv. We in this system, act as end-users and through the mobile app interact with Cloud (and in turn devices installed in our homes). A request will send to the cloud infrastructure with the authentication of the device and device information. It requires authentication of the device to ensure cybersecurity.
v. Once the cloud has authenticated the device, it sends a request to the appropriate sensor network using gateways.
vi. After receiving the request, the temperature sensor inside the AC will read the current temperature in the room and will send the response back to the cloud.
vii. Cloud infrastructure will then identify the particular user who has requested the data and will then push the requested data to the app. So, a user will get the current information about the temperature in the room, pick up through AC’s temperature sensors directly on his screen.

So, this was all about how IoT works. Hope you like our explanation.
4. Conclusion
Hence, today we learned how IoT works and an entire IOT system functions. Also, we discussed some real-life examples where we can use IoT. We will be learning more about IOT in detail in the upcoming tutorials. Till stay tuned to learn more interesting things. Furthermore, if you have any query, feel free to ask in the comment section.

