Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Iterative Model
An iterativelife cycle model does not attempt to start with a full specification of requirements. Instead, development begins by specifying and implementing just part of the software, which can then be reviewed in order to identify further requirements. This process is then repeated, producing a new version of the software for each cycle of the model.
For example:
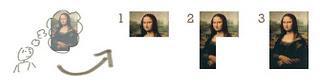
In the diagram above when we work iteratively we create rough product or product piece in one iteration, then review it and improve it in next iteration and so on until it’s finished. As shown in the image above, in the first iteration the whole painting is sketched roughly, then in the second iteration colors are filled and in the third iteration finishing is done. Hence, in iterative model the whole product is developed step by step.
Diagram of Iterative model:
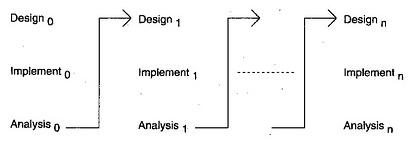
Advantages of Iterative model:
- In iterative model we can only create a high-level design of the application before we actually begin to build the product and define the design solution for the entire product. Later on we can design and built a skeleton version of that, and then evolved the design based on what had been built.
- In iterative model we are building and improving the product step by step. Hence we can track the defects at early stages. This avoids the downward flow of the defects.
- In iterative model we can get the reliable user feedback. When presenting sketches and blueprints of the product to users for their feedback, we are effectively asking them to imagine how the product will work.
- In iterative model less time is spent on documenting and more time is given for designing.
Disadvantages of Iterative model:
- Each phase of an iteration is rigid with no overlaps
- Costly system architecture or design issues may arise because not all requirements are gathered up front for the entire lifecycle
When to use iterative model:
- Requirements of the complete system are clearly defined and understood.
- When the project is big.
- Major requirements must be defined; however, some details can evolve with time.

