Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
- Dart Programming
- Flutter Tutorial
- Numerical Methods Tutorials
- VueJS
- Go
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
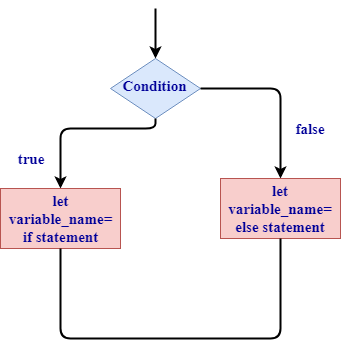
Using "if in a let" statement
An 'if' expression is used on the right hand side of the let statement and the value of 'if' expression is assigned to the 'let' statement.
Syntax of 'if in a let'
Let variable_name= if condition{
//code blocks
}
else{
//code block
}
In the above syntax, if the condition is true then the value of 'if' expression is assigned to the variable and if the condition is false then the value of 'else' is assigned to the variable.
Example 1
Let's see a simple example.
fn main()
let a=if true
{
1
}
else
{
2
};
println!("value of a is: {}", a);
Output:
value of a is: 1
In this example, condition is true. Therefore, 'a' variable bounds to the value of 'if' expression. Now, a consist 1 value.
Let's see a another simple example.
fn main()
let b=if false
{
9
}
else
{
"javaTpoint"
};
println!("value of a is: {}", a);
Output:
Some errors occurred:E0308
In this example, 'if' block evaluates to an integer value while 'else' block evaluates to a string value. Therefore, this program throws an error as both the blocks contains the value of different type.

