Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
Practical Paper
Industrial Training
Polymorphism and Virtual Functions
Virtual Function is a function in base class, which is overrided in the derived class, and which tells the compiler to perform Late Binding on this function.
Virtual Keyword is used to make a member function of the base class Virtual.
Late Binding
In Late Binding function call is resolved at runtime. Hence, now compiler determines the type of object at runtime, and then binds the function call. Late Binding is also called Dynamic Binding or Runtime Binding.
Problem without Virtual Keyword
class Base
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "Base class";
}
};
class Derived:public Base
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "Derived Class";
}
}
int main()
{
Base* b; //Base class pointer
Derived d; //Derived class object
b = &d;
b->show(); //Early Binding Ocuurs
}
Output : Base class
When we use Base class's pointer to hold Derived class's object, base class pointer or reference will always call the base version of the function
Using Virtual Keyword
We can make base class's methods virtual by using virtual keyword while declaring them. Virtual keyword will lead to Late Binding of that method.
class Base
{
public:
virtual void show()
{
cout << "Base class";
}
};
class Derived:public Base
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "Derived Class";
}
}
int main()
{
Base* b; //Base class pointer
Derived d; //Derived class object
b = &d;
b->show(); //Late Binding Ocuurs
}
Output : Derived class
On using Virtual keyword with Base class's function, Late Binding takes place and the derived version of function will be called, because base class pointer pointes to Derived class object.
Mechanism of Late Binding
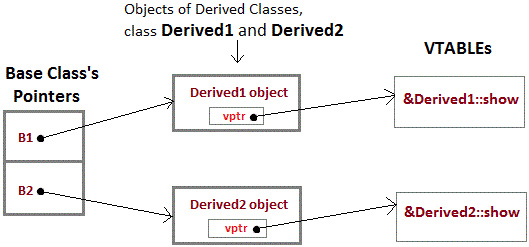
To accomplich late binding, Compiler creates VTABLEs, for each class with virtual function. The address of virtual functions is inserted into these tables. Whenever an object of such class is created the compiler secretly inserts a pointer called vpointer, pointing to VTABLE for that object. Hence when function is called, compiler is able to resovle the call by binding the correct function using the vpointer.
Important Points to Remember
Only the Base class Method's declaration needs the Virtual Keyword, not the definition.
If a function is declared as virtual in the base class, it will be virtual in all its derived classes.
The address of the virtual Function is placed in the VTABLE and the copiler uses VPTR(vpointer) to point to the Virtual Function.

