Theoretical Paper
- Computer Organization
- Data Structure
- Digital Electronics
- Object Oriented Programming
- Discrete Mathematics
- Graph Theory
- Operating Systems
- Software Engineering
- Computer Graphics
- Database Management System
- Operation Research
- Computer Networking
- Image Processing
- Internet Technologies
- Micro Processor
- E-Commerce & ERP
- Numerical Methods Tutorial
Practical Paper
- C Programming
- C
- Data Structure Using C, C ++
- Programming in R
- Programming with Python
- Machine Learning
- Swift
- Firebase
- Android
- iOS Development
- Django
- PHP
- Arduino
- Internet of Technology
- IOT Projects
- Dart Programming
- Flutter
- Flutter Tutorials
- Kotlin Tutorial
- Laravel Tutorial
- VueJS Tutorial
- Go Lang
- Rust
- Apex
Industrial Training
Looping
In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on. There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times.
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
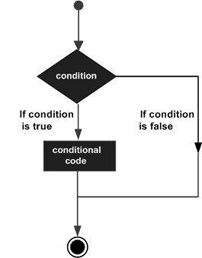
A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times. The following diagram illustrates a loop statement −
Python programming language provides following types of loops to handle looping requirements.
Sr.No. |
Loop Type & Description |
1 |
Repeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is TRUE. It tests the condition before executing the loop body. |
2 |
Executes a sequence of statements multiple times and abbreviates the code that manages the loop variable.. |
3 |
You can use one or more loop inside any another while, for or do..while loop. |
Loop Control Statements
Loop control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed.
Python supports the following control statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
Let us go through the loop control statements briefly
Sr.No. |
Control Statement & Description |
1 |
Terminates the loop statement and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop. |
2 |
Causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating. |
3 |
The pass statement in Python is used when a statement is required syntactically but you do not want any command or code to execute. |